DEXCOM G6 PLACEMENT: BEST SPOTS ON YOUR BODY TO WEAR IT
*Disclaimer: All content and information in this blog is for informational and educational purposes only.

Deciding where to attach your Dexcom G6 sensor can be a common dilemma among CGM users. While the FDA specifies certain approved locations for sensor placement, many individuals with diabetes have discovered alternative sites that offer reliable readings and improved comfort. These off-label site locations have gained popularity within the diabetes community, allowing individuals to customize their sensor placement based on personal preferences and experiences. Keep reading to discover the ideal spot to wear your Dexcom G6 sensor.

WHERE CAN I INSERT MY DEXCOM G6 SENSOR?
Accurate and reliable glucose readings are crucial for individuals using Dexcom G6 sensors, making proper sensor placement a key consideration. However, limitations such as skin irritation and other issues can make finding suitable sites challenging. Currently, Dexcom sensors have a limited number of FDA-approved locations, but the diabetes community has taken it upon themselves to explore alternative, non-FDA-approved sites for sensor placement. Here are some examples of Dexcom site locations:
FDA-APPROVED SITE LOCATIONS:
Dexcom G6 is FDA-approved for the use in either one or two locations, depending on the user’s age. All users can place the G6 sensor on the abdomen or back of the supper arm. Children (ages 2-17) are additionally approved to use it on the upper buttocks.
- Abdomen: The abdomen is a popular and convenient location. It offers good accuracy and is easily accessible for insertion and maintenance. Many individuals who have experience with insulin pumps on their bellies find it natural to place a CGM sensor there as well. The abdomen can also be a discrete location.
- Back of upper arm: The back of the upper arm is relatively easy to access and provides good accuracy. Many users prefer this location to avoid the sensor swiping against door frames. It is considered comfortable for sleeping, and the tricep muscle in this area tends to twist and flex less than the abdomen, potentially helping the adhesive stick longer.
- Upper buttocks: The upper buttocks can be a comfortable and discreet location for sensor placement. It may be suitable for individuals who prefer sleeping on their stomach or who use their abdomen for insulin pump sites.
DIABETES COMMUNITY SITE ALTERNATIVES:
Dexcom advises users to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for sensor placement, as they have conducted clinical testing and submitted data for the FDA approval specifically for those locations. However, it is worth noting that some individuals with diabetes choose alternative sites for their CGM placement due to factors such as comfort, discretion, durability, ease of application, and protection from accidental impacts. While these alternative sites have not officially been endorsed by the manufacturer, they have been experimented with by members of the diabetes community. Below are some examples of these alternative site locations:
- Front of arm: Placing the sensor on the front of the arm may help avoid signal loss caused by compression lows. This location is also less prone to snagging compared to the back of the arm, reducing the likelihood of the sensor being accidentally removed.
- Thigh: The thigh can be a convenient alternative site that is less obstructive than the arm. It also offers discretion and can be more comfortable than the abdomen for some individuals.
- Chest: Placing the sensor on the upper chest can be advantageous as this area undergoes less twisting and bending compared to the abdomen which can potentially enhance the adhesive's durability.
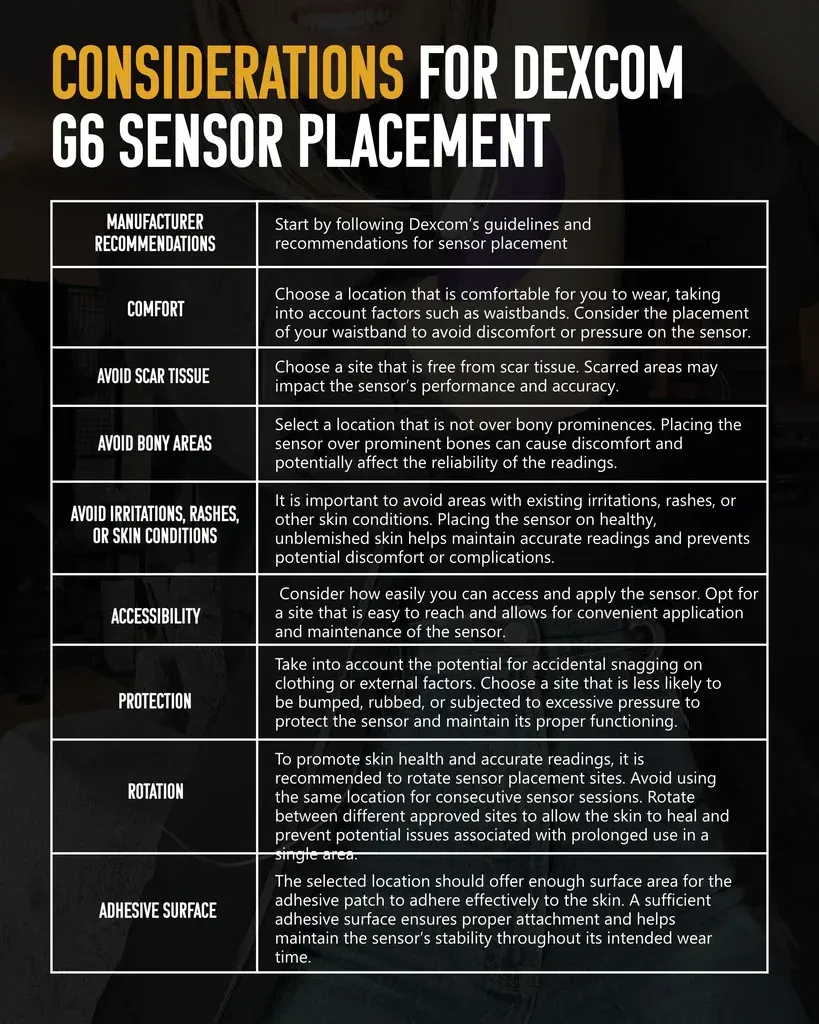
CONSIDERATIONS FOR DEXCOM G6 SENSOR PLACEMENT
When considering the sensor placement for your Dexcom G6, there are several important factors that you should consider:
- Manufacturer recommendations: Start by following Dexcom’s guidelines and recommendations for sensor placement.
- Comfort: Choose a location that is comfortable for you to wear, taking into account factors such as waistbands. Consider the placement of your waistband to avoid discomfort or pressure on the sensor.
- Avoid Scar Tissue: Choose a site that is free from scar tissue. Scarred areas may impact the sensor's performance and accuracy.
- Avoid Bony Areas: Select a location that is not over bony prominences. Placing the sensor over prominent bones can cause discomfort and potentially affect the reliability of the readings.
- Avoid Irritations, Rashes, or Skin Conditions: It is important to avoid areas with existing irritations, rashes, or other skin conditions. Placing the sensor on healthy, unblemished skin helps maintain accurate readings and prevents potential discomfort or complications.
- Accessibility: Consider how easily you can access and apply the sensor. Opt for a site that is easy to reach and allows for convenient application and maintenance of the sensor.
- Protection: Take into account the potential for accidental snagging on clothing or external factors. Choose a site that is less likely to be bumped, rubbed, or subjected to excessive pressure to protect the sensor and maintain its proper functioning.
- Rotation: To promote skin health and accurate readings, it is recommended to rotate sensor placement sites. Avoid using the same location for consecutive sensor sessions. Rotate between different approved sites to allow the skin to heal and prevent potential issues associated with prolonged use in a single area.
- Adhesive surface: The selected location should offer enough surface area for the adhesive patch to adhere effectively to the skin. A sufficient adhesive surface ensures proper attachment and helps maintain the sensor's stability throughout its intended wear time.
If you find it difficult to locate a CGM site that doesn't interfere with your daily activities, Skin Grip’s Dexcom G6 adhesive patches can provide an extra layer of protection to help keep your CGM securely in place throughout its intended wear time.

IS IT PAINFUL TO INSERT A DEXCOM G6 SENSOR?
The Dexcom G6 auto-applicator was specifically designed to improve the insertion process by making it easier and more comfortable compared to previous versions of Dexcom applicators. According to a survey conducted among Dexcom G6 users, 84% of respondents reported that the initial insertion with the auto-applicator was painless. Additionally, all respondents, representing 100% of the participants, reported that the applicator itself was easy to use. These findings indicate that the Dexcom G6 auto-applicator has been well-received by users, offering a positive experience during the insertion process.
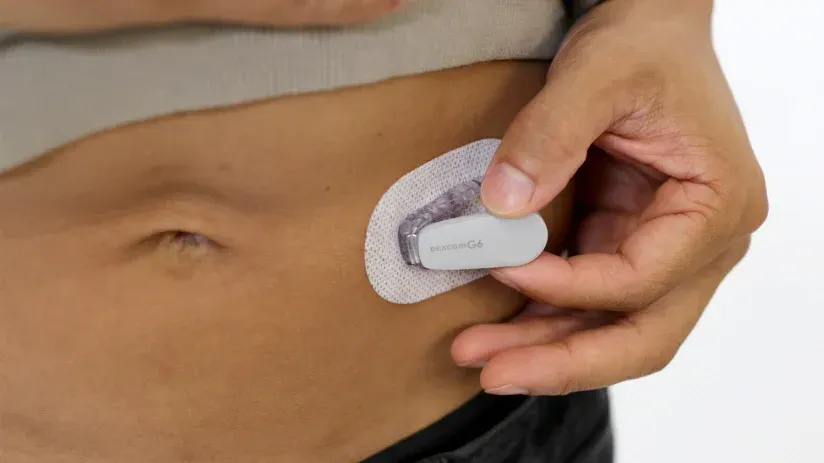
HOW DO I INSERT MY DEXCOM SENSOR?
Dexcom provides step-by-step instructions for sensor insertions on their website as well as on the users display device. It is important that Dexcom users take proper protocol steps before, during and after insertion to ensure the sensor stays on for the entire session.
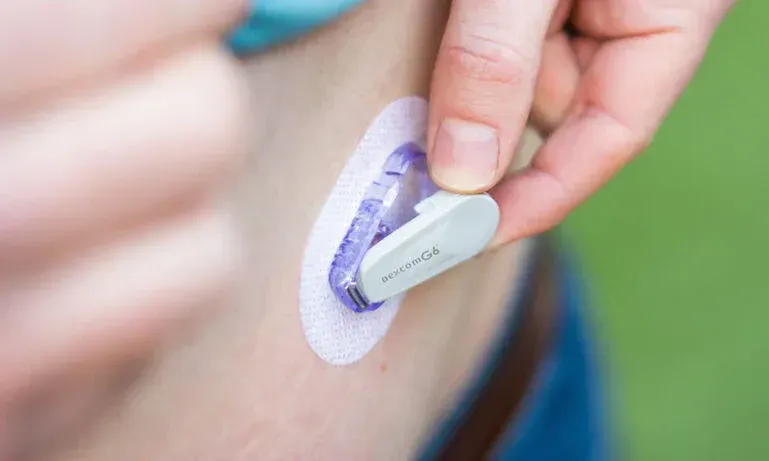
WHAT HAPPENS IF MY SENSOR INSERTION CAUSES BLEEDING?
In order to obtain glucose readings, the Dexcom G6 insertion needle needs to penetrate the dermis layer of the skin, which contains scattered blood vessels. If these blood vessels are pierced during insertion, it can cause bleeding. Additionally, if the sensor is inserted too deep, bleeding may occur as well.
Proper insertion technique plays a crucial role in preventing bleeding. When pressing the button on the applicator, ensure that the sensor is resting superficially on the surface of your skin. If you do encounter bleeding during the insertion process, it may not be necessary to immediately remove the sensor. However, if the bleeding continues or the site becomes painful, it is recommended to contact Dexcom customer support for assistance. They can provide guidance and support to address any concerns or issues you may have related to bleeding or discomfort.
This article was medically reviewed by Amanda Ciprich, MS, RD. Last updated on 7/17/23.
Source: www.skingrip.com
Healthy Bites